Table of Contents
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence has become the defining force of the digital era, powering everything from the search engines we rely on daily to the intelligent systems that are reshaping industries.
For businesses, understanding these stages is not just a matter of historical curiosity. As AI evolves, it undergoes distinct stages, each marked by significant milestones and capabilities as algorithms learn, adapt, and gradually simulate human intelligence.
In this article, we will go through the 7 stages of Artificial Intelligence to have a better understanding of the progression from basic rule-based systems to advanced machine learning and cognitive computing.
Stage One: Rule-Based AI Systems (1950s-1960s)
The origins of AI lie in rule-based systems, often referred to as expert systems. Emerging prominently in the mid-20th century, these systems followed if-then logic to perform tasks.
- Engineers and scientists created exhaustive sets of rules that described possible scenarios and corresponding outcomes.
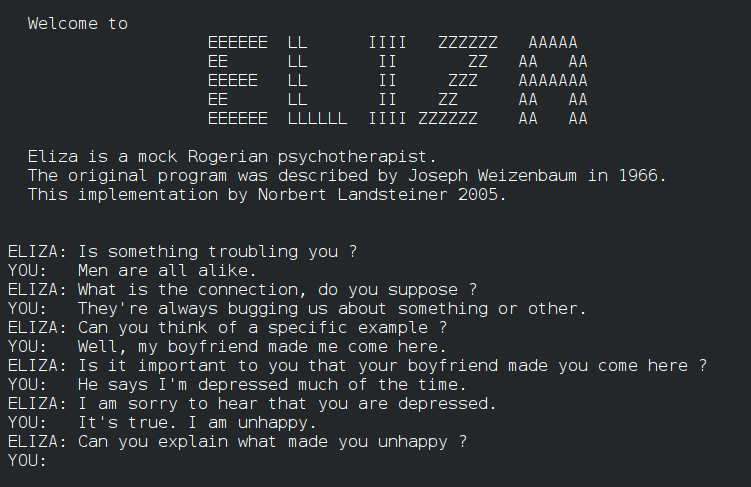
- One of the earliest examples was ELIZA (1966), a computer program that mimicked human conversation by responding to inputs with pre-programmed phrases.
- Another was MYCIN (1970s), which helped doctors diagnose bacterial infections based on a structured set of medical rules.
Key Characteristics
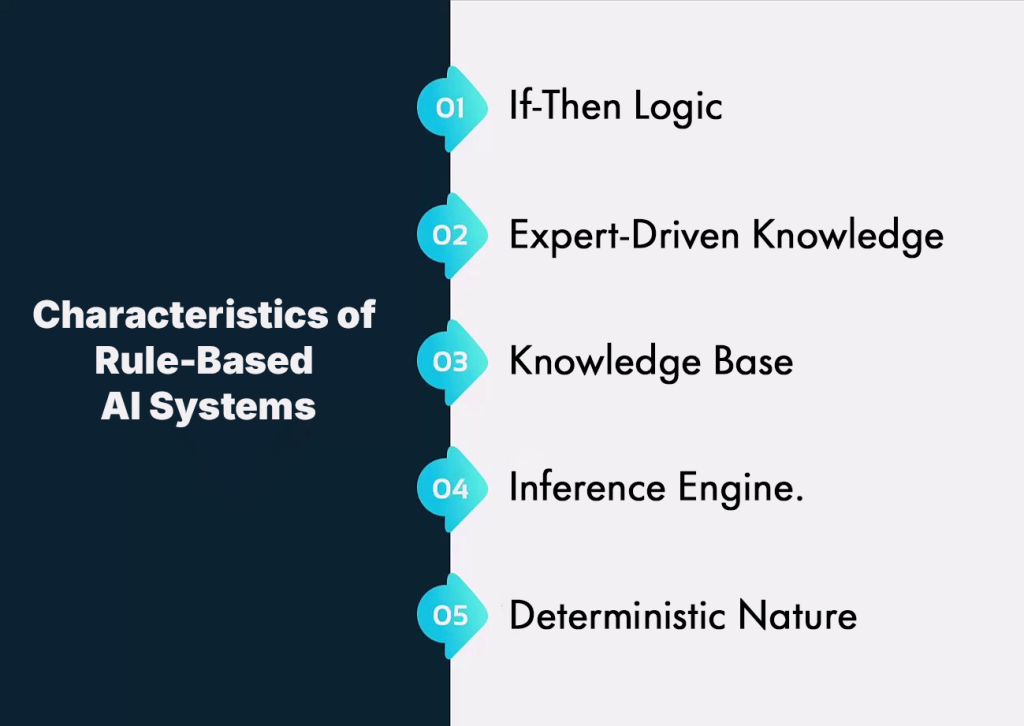
- If-Then Logic: Decisions follow clearly defined conditional rules that map specific inputs to outcomes.
- Expert-Driven Knowledge: Rules are derived from human expertise and tailored to domain-specific scenarios.
- Knowledge Base: A structured repository containing facts and rules that guide the system’s decisions.
- Inference Engine: The mechanism that applies stored rules to incoming data to generate conclusions.
- Deterministic Nature: Always produces the same result for identical inputs, ensuring consistency.
The logic is easy to trace and explain, making the system’s decision-making understandable and trustworthy.
Stage Two: Context Awareness and Retention (1990s- 2000)

The next step in AI’s evolution was the ability to retain context and learn from past interactions.
- Unlike rule-based systems that reset after every task, these systems could remember what had happened before and use that memory to refine their outputs.
- One of the most visible examples of this stage appeared in virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
- Similarly, customer support chatbots started using memory to improve interactions, ensuring users didn’t need to repeat themselves every time they returned.
Key Characteristics

- Pattern Recognition: AI starts identifying patterns and logic within data, moving beyond simple, static rules.
- Information Retention: Systems can store and recall past information and previous interactions, forming a kind of memory.
- Contextual Understanding: The AI uses retained information and the current context to make more informed and relevant decisions or responses.
- Foundation for Advanced AI: This stage is a critical step, bridging the gap from rule-based systems to more sophisticated forms of AI that can adapt and learn.
- Learning from Data: Unlike earlier systems, these systems don’t need explicit programming for every situation; they learn and adapt by processing new data.
Stage Three: Domain-Specific AI - ANI (2000s-2010s)
By the 2000s and 2010s, AI had entered the era of Domain-Specific Mastery Systems, marked by increasing specialization within particular fields.

- A defining achievement of this period was IBM’s Watson, unveiled in 2011.
- The project was spearheaded by a dedicated team of researchers and engineers, with David Ferrucci playing a leading role in its development
- The arrival of Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) brought systems capable of achieving superhuman performance in tightly defined domains.
- Another iconic breakthrough was AlphaGo, developed by DeepMind, which defeated the world champion in the complex game of Go—a feat previously thought decades away.
Key Characteristics
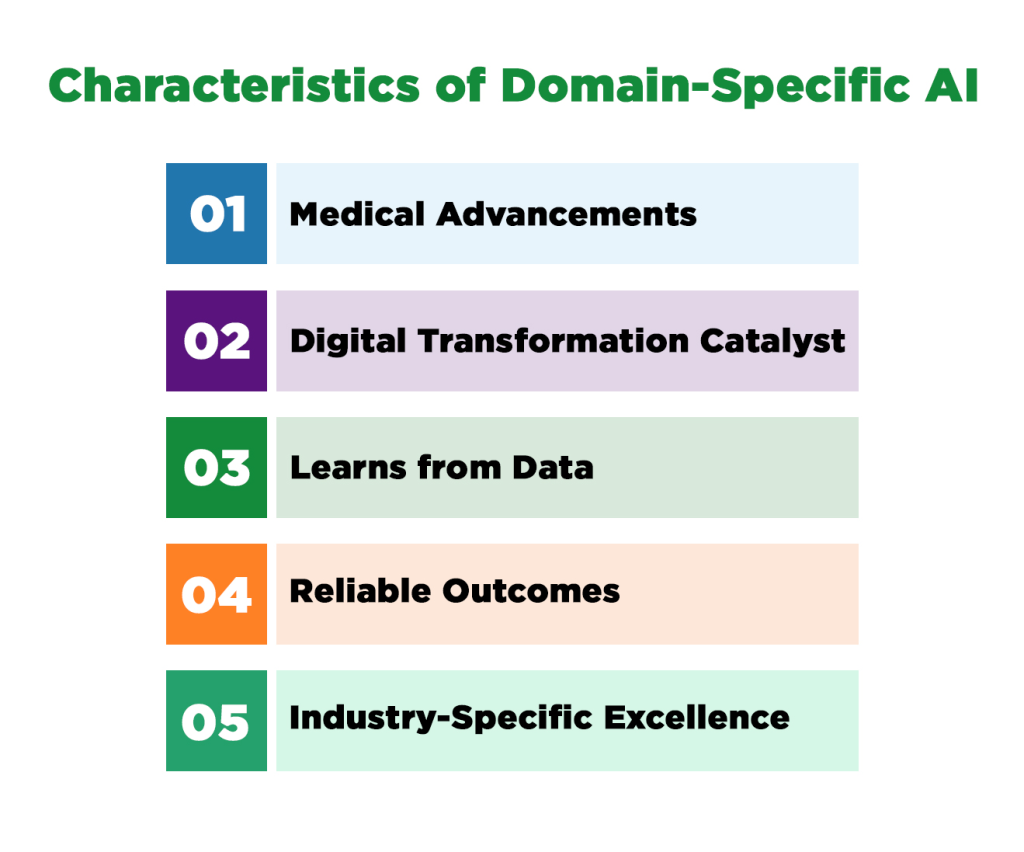
- Medical Advancements: ANI systems have transformed healthcare by analyzing X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with precision that often surpasses that of human radiologists.
- Digital Transformation Catalyst: ANI has become a cornerstone of enterprise digital strategies, driving measurable ROI across various industries. Its speed, accuracy, and scalability positioned it as a powerful tool for innovation.
- Learns from Data: These systems use mathematical algorithms and statistical models to analyze data, identify patterns, and improve their performance over time within their designated domain.
- Reliable Outcomes: Pre-trained data and focused algorithms lead to more reliable and trustworthy results for the specific tasks they are designed to perform.
- Industry-Specific Excellence: ANI systems excelled in specialized domains—analyzing medical images with near-human precision, powering high-frequency trading in finance, and detecting fraudulent activities in cybersecurity.
Stage Four: Thinking and Reasoning AI Systems (Present)
In the current stage of AI evolution, we see the rise of Thinking and Reasoning Systems, where machines strive to replicate aspects of human cognition.
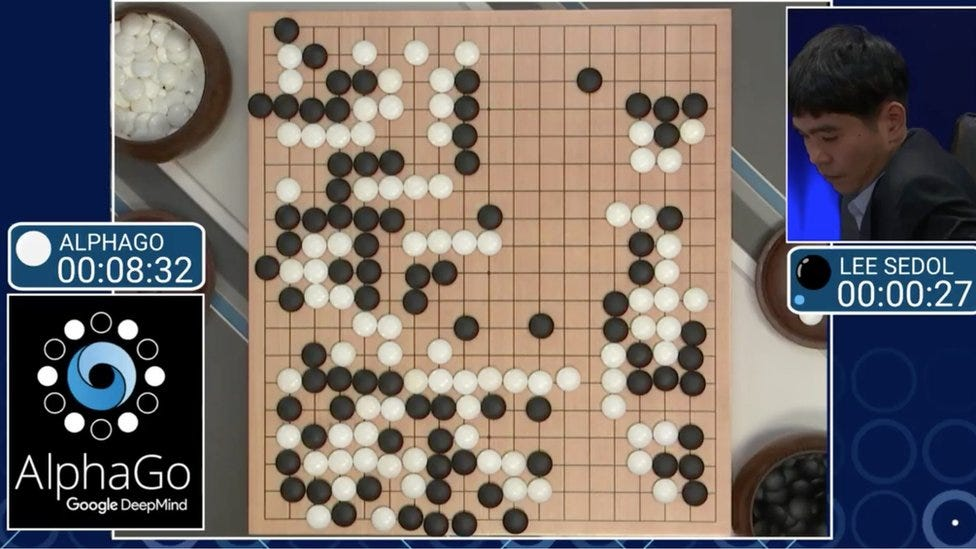
- This era has been defined by groundbreaking achievements, most notably DeepMind’s AlphaGo.
- Launched in 2016 under the leadership of Demis Hassabis and his research team, AlphaGo represented a paradigm shift in the capabilities of artificial intelligence.
Key Characteristics
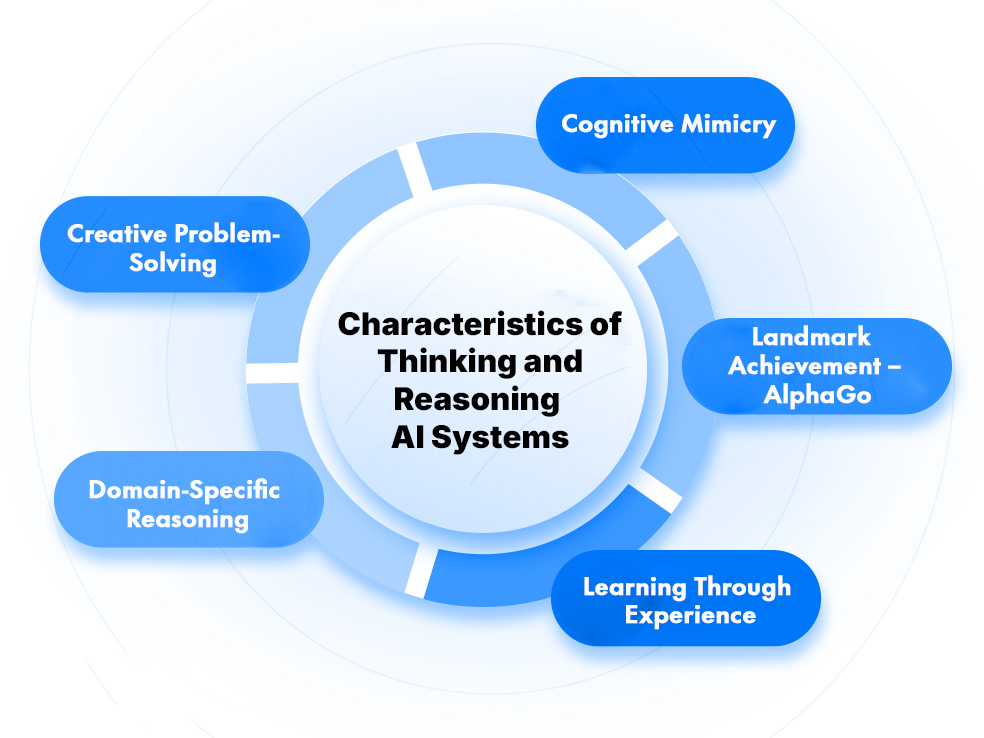
- Cognitive Mimicry: AI systems in this stage attempt to replicate human-like cognitive processes, moving beyond simple rule-following to reasoning, strategizing, and adapting.
- Landmark Achievement – AlphaGo: DeepMind’s AlphaGo (2016) demonstrated the power of machine learning and deep learning by defeating world champions in the complex game of Go, showcasing creativity and adaptability.
- Learning Through Experience: These systems rely on neural networks and reinforcement learning, enabling them to anticipate outcomes, adjust strategies dynamically, and improve performance with continued exposure.
- Creative Problem-Solving: Reasoning AI introduces the ability to formulate novel solutions, such as AlphaGo’s unexpected but highly effective moves, proving machines can innovate within defined domains.
- Domain-Specific Reasoning: While powerful in specialized areas, these systems remain limited in scope, excelling in one context but unable to transfer reasoning seamlessly across domains.
Businesses are beginning to view these systems as partners rather than tools, extending human capabilities into new realms of scale and efficiency.
Stage Five: Artificial General Intelligence - AGI (Present)
At present, Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) represents a pivotal milestone in AI’s trajectory, aiming to create machines with human-like adaptability across a wide range of tasks.
- Although true AGI remains largely theoretical, a prominent step in this direction is OpenAI’s Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), first introduced in 2020.
- GPT demonstrates an impressive scope of abilities, excelling in natural language comprehension, creative content generation, and even software code development.
Key Characteristics
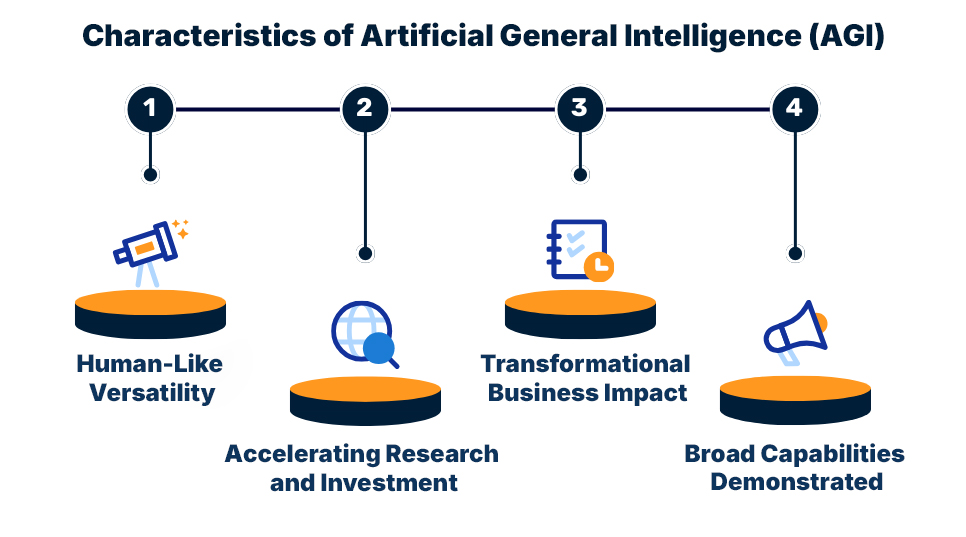
- Human-Like Versatility: AGI aspires to achieve generalized intelligence, enabling machines to perform a wide range of cognitive tasks across different domains with adaptability similar to human reasoning.
- Broad Capabilities Demonstrated: Models like OpenAI’s GPT highlight early progress by handling diverse tasks—natural language understanding, content creation, and even programming—showcasing the breadth that AGI aims for.
- Accelerating Research and Investment: Leading organizations such as OpenAI, DeepMind, and Anthropic are investing heavily in architectures and frameworks that could eventually deliver true AGI.
- Transformational Business Impact: AGI holds the potential to redefine industries, shorten innovation cycles from years to weeks, optimize global logistics, and address large-scale challenges like climate change.
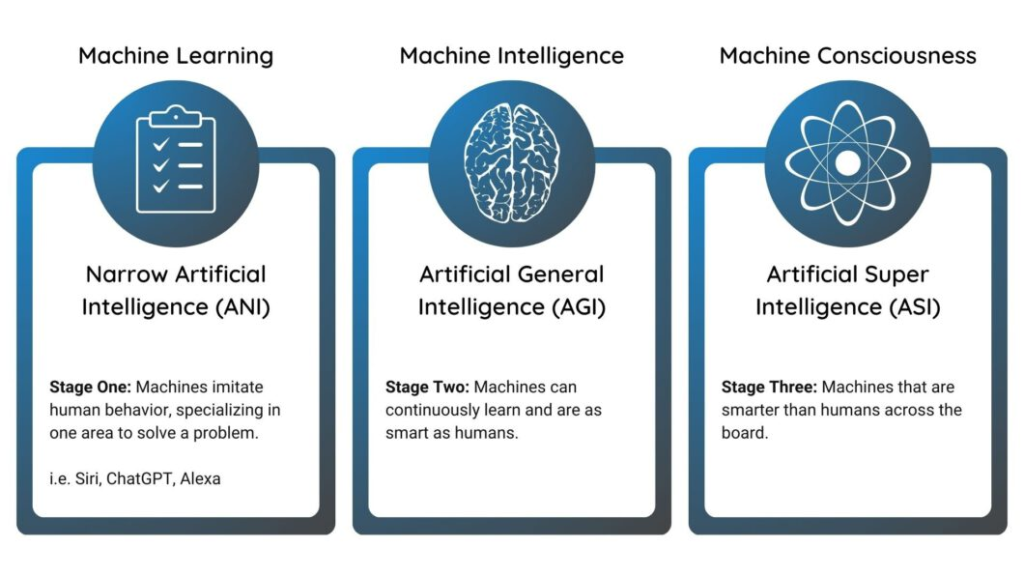
Stage Six: Artificial Super Intelligence - ASI (Future)
Stage 6 of AI, known as Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), is still only a theory.
- It describes a future where AI could become smarter than humans in every way—a point often called the technological singularity.
- Thinkers like Nick Bostrom and Eliezer Yudkowsky have explored this idea. While no real examples exist yet, the possibility of ASI brings both excitement and concern about what it could mean for humanity.
Key Characteristics
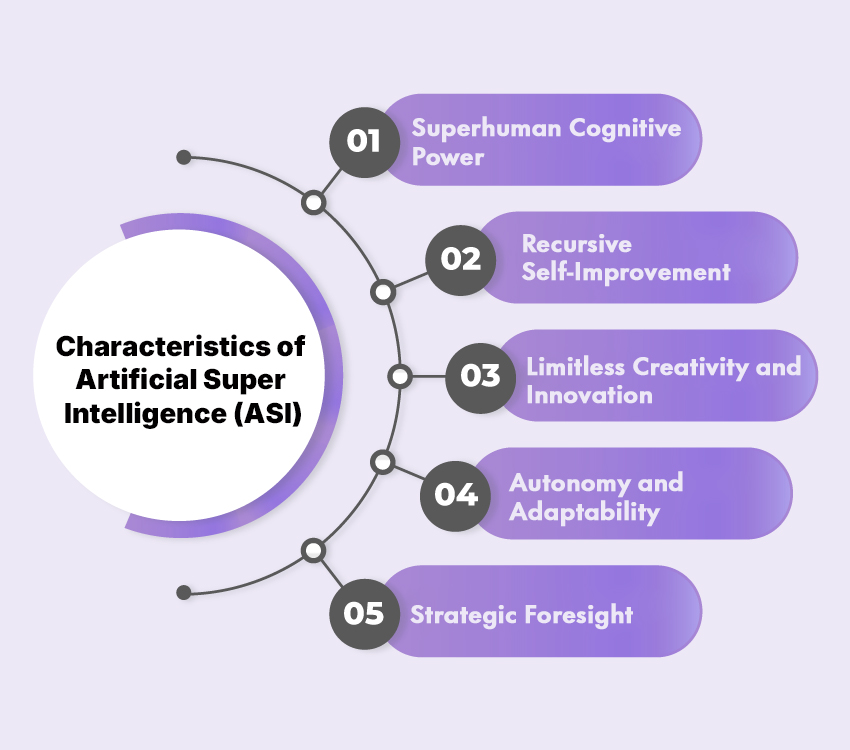
- Superhuman Cognitive Power: ASI could analyze data at extreme speed and accuracy, surpassing human reasoning across all fields.
- Recursive Self-Improvement: It could continually upgrade itself, leading to an exponential rise in intelligence.
- Limitless Innovation: ASI might achieve breakthroughs in science, technology, and solutions for global issues.
- Autonomy and Adaptability: Able to operate independently and handle new tasks without reprogramming.
- Strategic Foresight: By simulating vast scenarios, it could create long-term, unbiased strategies.
Stage Seven: The AI Singularity (Hypothetical Future)
The final and speculative stage, the AI Singularity, postulates a future point where technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, leading to unforeseeable changes in human civilization.
Coined by futurist Ray Kurzweil, the term “singularity” is reminiscent of a point where AI, particularly Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), achieves unprecedented advancement.
Key Characteristics

- Recursive Self-Improvement: Superintelligent AI could continually upgrade itself, triggering a rapid intelligence explosion with each generation becoming smarter.
- Irreversible Change: The pace of progress would outstrip human control, making outcomes unpredictable and unstoppable.
- Beyond Human Understanding: Advances would be so complex that their logic and reasoning would be incomprehensible to humans.
- Shift of Power: Humanity would no longer be the most intelligent force—self-improving AI would drive progress and innovation.
Even if the singularity remains theoretical, preparing for its potential outcomes forces businesses to confront fundamental questions about leadership, governance, and purpose in an AI-dominated future.
Conclusion
The journey through the seven stages of Artificial Intelligence highlights an extraordinary progression in how machines are learning to mirror—and in some areas, surpass—human intelligence.
Each stage demonstrates the boundless potential of AI, driven by innovation, data, and adaptive learning, pushing us toward a future where possibilities continue to expand. At the same time, this evolution brings responsibilities: to remain mindful of the ethical, societal, and governance challenges that come with such powerful technology.
As AI advances from simple rule-based systems to visions of general intelligence and beyond, it is steadily transforming industries, science, and daily life. The seven stages chart not only a technological roadmap but also a call for balance—embracing AI’s transformative promise while staying vigilant about its risks.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



